Risk Management is the identification, assessment, and prioritisation of risks followed by coordinated and economical application of resources to minimize, monitor, and control the probability or impact of unfortunate events or to maximize the realization of opportunities. Risk management is an ongoing process that is essential for any organization that wants to operate effectively and efficiently.
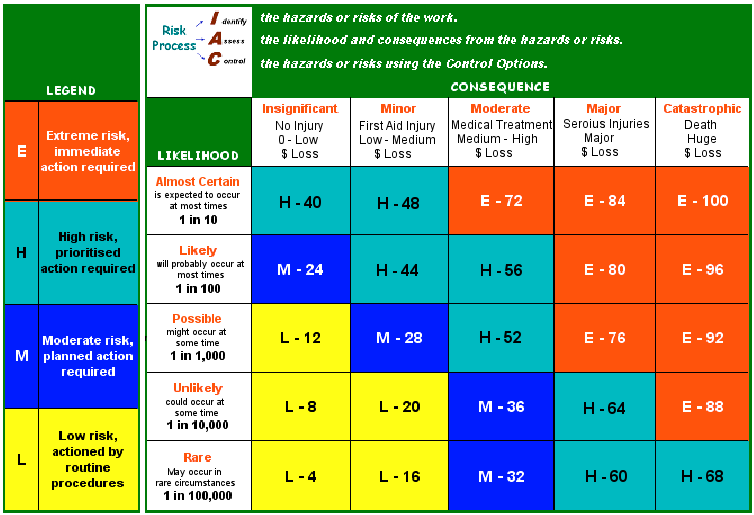
The goal of risk management is to protect the organisation from potential losses and to ensure that it achieves its objectives. Risk management can be applied to all aspects of an organisation, including its operations, finances, and reputation.
There are many different types of risks that an organisation can face, including financial risks, operational risks, and reputational risks. Financial risks are those that could impact the organization's financial performance, such as changes in interest rates or currency exchange rates. Operational risks are those that could impact the organisation's ability to operate effectively, such as disruptions to its supply chain or IT systems. Reputational risks are those that could damage the organisation's reputation, such as a product recall or a data breach.